3/7/2023
SHIPNEXT launches a solution for Instant Emission Indexing

In the last 2-3 months, the formula proposed by the IMO was widely criticised. CEOs of a number of large and reputable Shipping companies have expressed their concern and disapproval. Examples were shown how the highest consuming vessels can actually get show a “greener” footprint and a higher CO2 emission at the same time. This is why Shipnext decided to propose a well-grounded and transparent solution.
Shipnext Voyage Emission Index (SVEI) – Emission index based on the individual technical parameters of the vessel, its speed, consumption and intake, that also takes into consideration the actual cargo quantity and the intended voyage. SVEI is based on the calculation of the Shipnext Carbon intensity indicator (SCII), according to the formula below.
This approach would stimulate Shipowners and Charterers to optimise intake and increase the efficiency of the way they manage their fleet with the aim of minimising ecological footprint. In other words, the overall effect of minimising carbon emissions would be reached through reduced ballast runs and optimised intake.
Shipnext proposes an approach that takes into account the ship’s fuel consumption at sea, since it reflects the work of the particular vessel and, while minimizing distance in ballast, creates opportunities for saving fuel and reducing CO2 emissions. Fuel consumption in the port is ignored, since the fuel consumption rates at port are comparable for most ships, and the time of loading and discharging is determined mainly by port technology not by the technical capabilities of the vessel. Moreover, the actual consumption of the auxiliary or main engine, or shore power cannot be defined or tracked during the voyage planning.
The combustion of 1 liter of diesel fuel produces about qCO2 = 2.68 kg. So, each liter of Diesel = 0.00268 tons of CO2.
1 ton of diesel fuel contains about 1185 liters, therefore burning 1 ton of diesel fuel: 1185 * 0.00268 = 3.1758 tons of CO2 is released.
We propose the following approach for calculating the CO2 index:
For a specific ship-cargo pair with certain voyage parameters, we calculate the fuel consumption in a voyage at sea in load and ballast condition and obtain Qfuel:
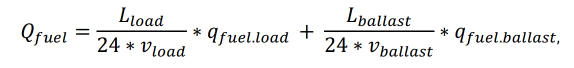
where:
L – distance in load and ballast condition, nmiles;
v – speed of vessel, knots (nmiles per hour);
q – fuel consumption in a voyage at sea in load and ballast condition, tons per day.
So, the CO2 emission will be for a specific voyage, tons per voyage:
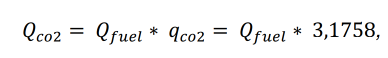
Next, we calculate the CO2 emission rate per 1 ton of transported cargo.
1) For sole cargo:
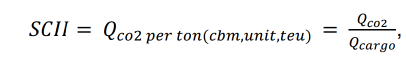
tons CO2 per 1 ton (1 m3, 1 unit or 1 TEU) of cargo.
2) For part cargoes we propose following approach (under part cargo we mean that which can be transported together with other cargoes on the same vessel):
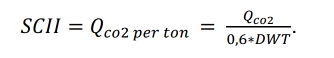
2.1. General cargo:
If Qcargo < 75% from DWT (deadweight of vessel):
• < 25% – divide the result of above formula by 4;
• 25 – 50% – divide the result of above formula by 3;
• 50+ – 75% – divide the result of above formula by 2.
2.2. Bulk cargo:
If Qcargo < 60% from DWT (deadweight of vessel, tons):
The only difference between EEOI and SCII is the fact that EEOI is calculated in “quantity of CO2 produced per mt of cargo per mile”, whereas SCII expresses this index “quantity of CO2 produced per mt of cargo”, but the duration of voyage, distance travelled and actual fuel consumed/CO2 produced is calculated in both cases, so the end result is the same.
Shipnext has patented and launched a platform that allows instant freight-matching (cargo-to-ship and ship-to-cargo matching). The algorithm takes into consideration hundreds of factors that allow an instant overview of the best matching fleet, and the possibility of sorting them by such criteria as the duration of ballast, dead-weight, etc. The emission level of each vessel is thus instantly calculated, based on the total bunker consumed for each particular potential voyage, and is taken in proportion to the cargo quantity, and can be easily compared before voyage planning.